Managing Roles¶
Watch video.
Manage roles from the Manage Roles page in the QDS Control Panel.
A role consists of one or more policies; a policy specifies a resource and the actions that can (or cannot) be performed on it; see Resources, Actions, and What they Mean. Assign roles to groups on the Manage Groups page. When inviting new users to join the account (via the Manage Users page), you can assign them to any existing group; the roles assigned to that group control what the user can do.
The sections that follow provide more information:
- System-defined Roles
- User-defined Roles
- Resources, Actions, and What they Mean
- Adding, Removing, and Modifying Roles
System-defined Roles¶
QDS creates these roles for every account:
- system-admin - Provides full access to all QDS resources, via a group with the same name. When you sign up for a free trial of QDS, you are assigned to the System-admin group by default.
- system-user - Allows users who belong to the group with this name to perform a more restricted set of actions, as shown on the Manage Roles page. This set of capabilities includes read access to every QDS resource, and should be sufficient for most QDS users who are not system administrators.
User-defined Roles¶
In addition to these system-defined roles, you can create roles to control access to specific resources. Assign a role to a group to control the actions of the users in that group. You can remove or modify any role you create.
When creating a new role, you may find it easiest to clone an existing role, then modify it by adding, removing, or changing policies. (You can’t directly modify the System-admin or System-user roles.)
Resources, Actions, and What they Mean¶
This section lists QDS resources (Account, Commands, etc.), the actions (create, read, update, etc.) that can be controlled on each (Access allowed or denied), and the effect of allowing or denying each action.
Points to Note¶
The default state of access for all actions on all resources is deny: if you don’t include a resource in a policy, all forms of access to that resource are denied by that policy; similarly, if you include a resource, only the actions you specifically allow are allowed by that policy for that resource.
If policies within a role conflict, explicitly or implicitly, the most restrictive policy takes precedence. This is useful for creating exceptions.
For example, if a role includes a policy that specifies allow, Cluster, all, and another policy that specifies deny, Cluster, terminate, users belonging to a group that has that role will be able to perform all cluster tasks except stopping a cluster. Similarly, if you wanted to create a role that confers broad, but not unlimited capabilities, you could start out by cloning the system-admin role, and then explicitly deny access to certain resources, or certain actions on certain resources. For example, a role containing the two policies allow, All, all and deny, Account, all allows members of the group that has that role to do everything in QDS except see and manage account settings.
By contrast, when two or more roles that contain conflicting policies are assigned to the same group, the least restrictive role applies. For example, if Role1 denies create access to commands and Role2 allows it, and both roles are assigned to Group-DS, Role2’s policy takes precedence, allowing users in Group-DS to create and run commands.
Resources and Actions¶
All:
- all
- allow: allows all actions on all the resources listed below, providing complete control over the QDS resources in this account. By default, the person who originally signed up for the QDS account has this capability, by virtue of belonging to the system-admin group.
- deny: denies all access to QDS. (But it’s better to simply disable the user from the Manage Users page.)
- create - allows or prevents the create action on all QDS resources that support it.
- read - allows or denies read-only access to all QDS resources.
- update - allows or prevents the update action on all QDS resources that support it.
- delete - allows or prevents the delete action on all QDS resources that support it.
- all
Account:
These capabilities are normally reserved for the system-admin role. The system-user role allows only read access to account settings.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on the Account Settings and My Accounts pages in the QDS Control Panel.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to the account settings for this account.
- update - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on this account on the Account Settings page.
- auth_token - allows or prevents the visibility of API tokens and the access to reset the API tokens. API tokens provide the access to APIs and users should have the API tokens to access APIs.
App:
These capabilities relate to the actions that can be performed on Spark applications by means of the Spark application server.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on Spark applications.
- create - allows or prevents creating Spark applications. The system-user role allows creating applications.
- read - allows or denies read-only access to Spark applications.
- start - allows or prevents starting Spark applications.
- stop - allows or prevents stopping Spark applications.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting Spark applications.
Clusters:
Cluster configuration is normally reserved for the system-admin role. The system-user role allows viewing and starting clusters, but not creating, modifying, stopping or deleting them.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on the Clusters page in the QDS Control Panel.
- create - allows or prevents creating new clusters.
- read - allows or prevents viewing configured clusters on the Clusters page.
- update - allows or prevents modifying existing clusters.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting clusters.
- start - allows or prevents starting clusters manually. The system-user role allows this. (Many commands, such as Hadoop and Spark commands, can start a cluster automatically; that happens independently of this setting. Users who are allowed to run commands will have clusters started for them as needed.)
- terminate - allows or prevents stopping clusters manually. (By default, idle clusters are shut down automatically.)
- clone - allows or prevents cloning clusters.
Commands:
You can allow or deny the following actions on all types of command supported by QDS (as shown on the Workbench page), or on one or more types you specify here (via the field labelled Select a command type).
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on the command type(s) you specify, or on all command types. For example, a policy specifying Allow, Commands, Hive Query, all allows one to create, read, update, and delete Hive queries.
- create - allows or prevents creating commands of the specified type(s), or all types. For example, a policy specifying Allow, Commands, create (but not specifying any command type) allows one to create any type of command or query; this policy is part of the system-user role.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to the specified specified command type(s), or all types. For example, a policy specifying Allow, Commands, Hive Query, read allows one to see Hive queries that have been run, and their output, but not to run, modify, or delete them.
- update - allows or prevents modifying commands of the specified type(s), or all command types. For example, a policy specifying Allow, Commands, update allows a user to kill a command or query issued by another user.
- delete - deprecated; has no effect.
Data Preview:
You can use the Data Preview resource to restrict the visibility of sensitive data on the Qubole UI.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to data in the Qubole user interface on the Explore, Analyze, and Notebooks screens.
Data Connections:
Apart from read, Data Connection actions are normally reserved for the system-admin role.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on data stores.
- create - allows or prevents creating data stores.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to data stores. The system-user role allows only this type of access.
- update - allows or prevents updating data stores.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting data stores.
Data Connection Templates:
Apart from read, Data Store actions are normally reserved for the system-admin role.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on data stores.
- create - allows or prevents creating data stores.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to data stores. The system-user role allows only this type of access.
- update - allows or prevents updating data stores.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting data stores.
Environments and Packages:
Apart from read, Environments and Packages are normally reserved for the system-admin role.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on Package Management environments.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to Package Management environments.
- update - allows or prevents write access to Package Management environments.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting a Package Management environment.
- manage - allows or prevents editing Access Control Lists (ACLs) on Package Management environments. This capability allows one to extend or prevent other users’ access to the Package Management environment, and is granted to the system-admin role by default.
Folder:
These actions pertain to notebook folders and Notebook Dashboards, and apart from read, are normally reserved for the system-admin role.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on notebook folders.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to notebook folders.
- write - allows or prevents write access to notebook folders.
- manage - allows or prevents editing Access Control Lists (ACLs) on notebook folders. This capability allows one to extend or prevent other users’ access to the folders, and is granted to the system-admin role by default.
Groups:
Apart from read, actions related to managing groups are normally reserved for the system-admin role.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on groups.
- create - allows or prevents creating a group.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to groups.
- update - allows or prevents modifying a group.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting a group.
Notes:
The system-admin role is allowed all Notes actions.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on Notebooks.
- create - allows or prevents creating notes and notebooks.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to notebooks.
- update - allows or prevents modifying notes and notebooks.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting notes and notebooks.
Jupyter Notebook:
The system-admin role is allowed all Jupyter Notebook actions.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on Jupyter Notebooks.
- create - allows or prevents creating Jupyter notebooks.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to Jupyter notebooks.
- update - allows or prevents modifying Jupyter notebooks.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting Jupyter notebooks.
Notebook Dashboards
The system-admin and the associated notebook owners roles are allowed all actions on a dashboard.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on Dashboards.
- create - allows or prevents creating dashboards.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to dashboards.
- update - allows or prevents modifying dashboards.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting dashboards.
- execute - allows or prevents executing dashboards.
Object Storage
These capabilities relate to the actions you can perform on your QDS account’s Cloud storage, using the QDS Explore page (see the AWS or Azure instructions) or from the Analyze or Notebooks page.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on the storage. By default, the system-admin role has this policy.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to the storage. By default, the system-user role has this policy.
- upload - allows or prevents uploading a file.
- download - allows or prevents downloading a file.
Quest
The system-admin role is allowed all Quest actions.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed from the quest-index UI.
- create - allows or prevents creating streaming pipelines.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to the streaming pipelines.
- update - allows or prevents modifying streaming pipelines.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting streaming pipelines.
Roles:
Apart from read, actions related to managing roles, as described on this page, are normally reserved for the system-admin role.
- all - allows or prevents all the actions described on this page.
- create - allows or prevents adding policies and roles.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to roles.
- update - allows or prevents modifying roles.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting roles.
Scheduler:
- all - allows or prevents all the actions that can be performed on the Qubole Scheduler.
- create - allows or prevents creating a new job in the scheduler. The system-user role allows this.
- read - allows or prevents read-only access to the scheduler.
- update - allows or prevents modifying jobs in the scheduler.
- delete - allows or prevents deleting jobs in the scheduler.
- clone - allows or prevents cloning jobs in the scheduler. The system-user role allows this.
Schedule Instance:
The system-user role allows these actions:
- all - allows or prevents killing and re-running scheduled jobs.
- kill - allows or prevents killing scheduled jobs.
- rerun - allows or prevents re-running scheduled jobs.
Users:
Apart from read, actions related to managing users are normally reserved for the system-admin role.
- all - allows or prevents viewing and managing account users.
- read - allows or prevents viewing account users.
- manage - allows or prevents managing account users.
Adding, Removing, and Modifying Roles¶
Creating a Role¶
Click the add icon ![]() to create a new role. The Create a New Role page is displayed as shown in the
following figure.
to create a new role. The Create a New Role page is displayed as shown in the
following figure.
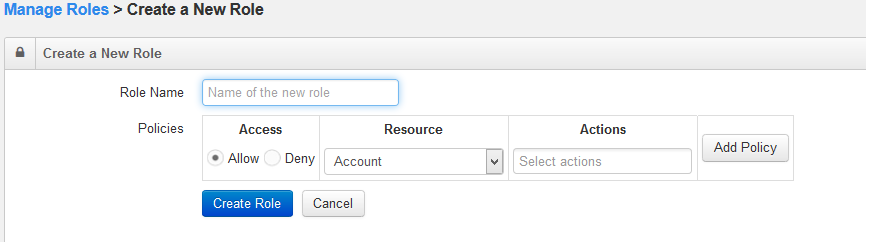
Enter a name in the Role Name text field. Add a new policy to the role. In the Policies field, select either Allow or Deny access.
Select a resource from the Resource drop-down list. Select one or more actions, all/create/read/update from the Action drop-down list.
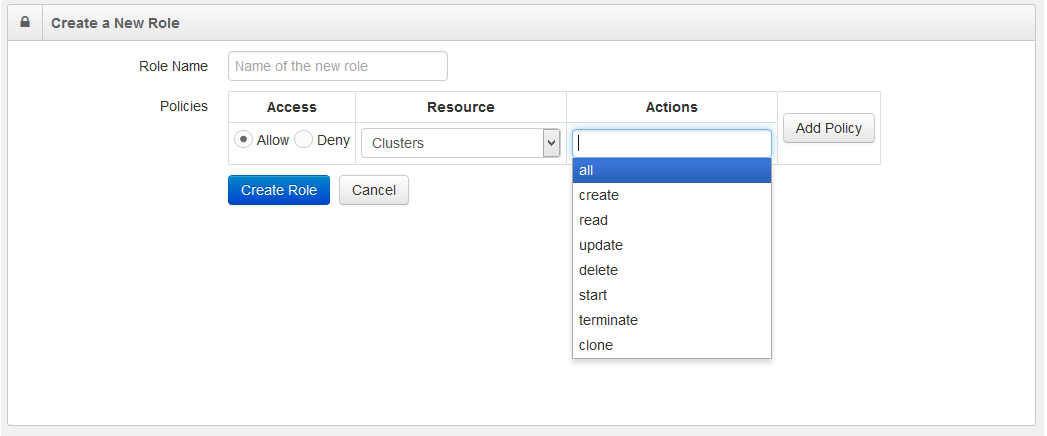
Qubole supports create, update, delete, start, terminate, and clone actions that a role can perform on a cluster as shown in the following figure.
Qubole supports selecting the command type when adding/editing a policy to a role. To set a command type, select Command resource and a new text field for command type appears as shown in the following figure.
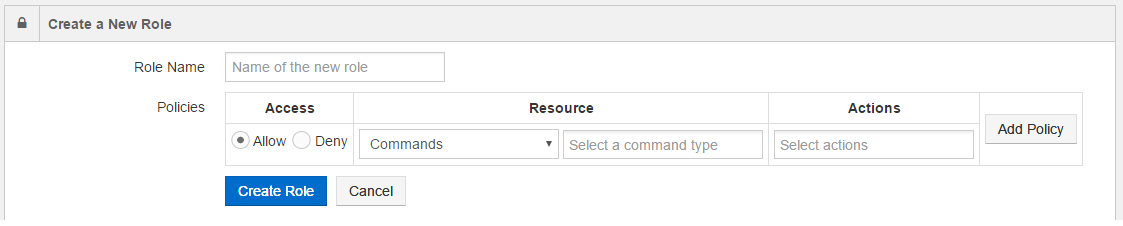
A mouse-click in the text field displays the list of command types. You can add more than one command type in the text field. You can also select create/read/update/delete actions from the Actions text field.
Click Add Policy to add a new policy for the new role. You can add more than one policy to a role.
For example, to create a policy to allow only Hive and Presto queries, perform the following steps:
Note
Presto is not currently supported on all Cloud platforms; see QDS Components: Supported Versions and Cloud Platforms.
By default Allow is selected in Access.
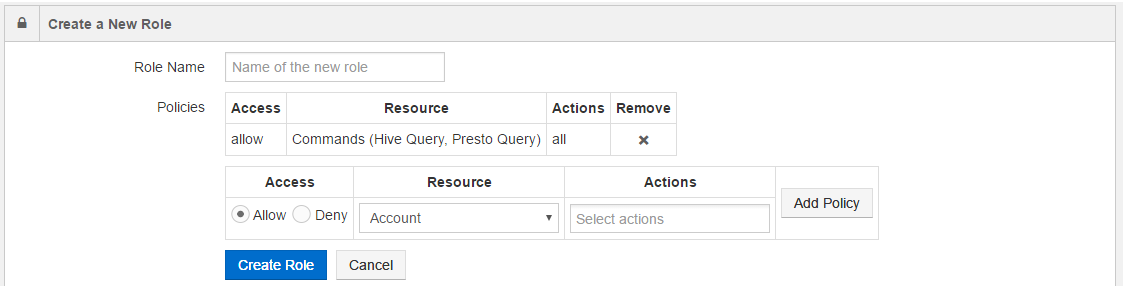
Select Commands in Resources and select Hive Query and Presto Query from the command type text field. The following figure shows selecting more than one command type.
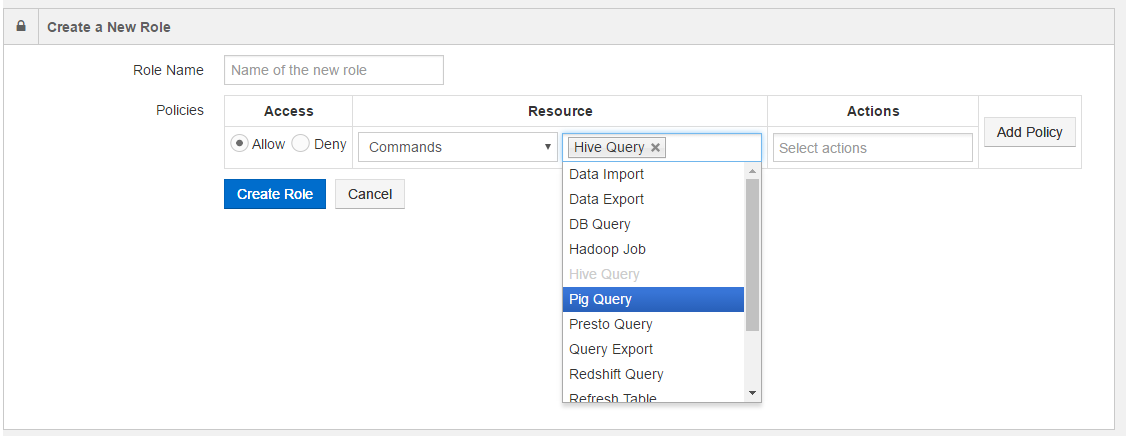
Select actions in the Actions text field.
Click Add Policy. The policy details are displayed as shown in the following figure.
As an another example, let us consider denying access to only Hive and Presto command types in a policy. Perform the following steps:
- In Access, let Allow be selected by default.
- In Resources, select Commands. This would allow access to all command types.
- Select actions in the Actions text field.
- Click Add Policy.
- In Access, select Deny (that has Allow selected by default).
- In Resources, select Commands.
- In the command-type text field, select Hive Query and Presto Query.
- Select actions in the Actions text field.
- Click Add Policy.
This policy would deny access to only Hive and Presto command types. (You create two policies when you want to deny one or two command types from the list of supported command types).
The following figure shows an example of adding a policy to a role.
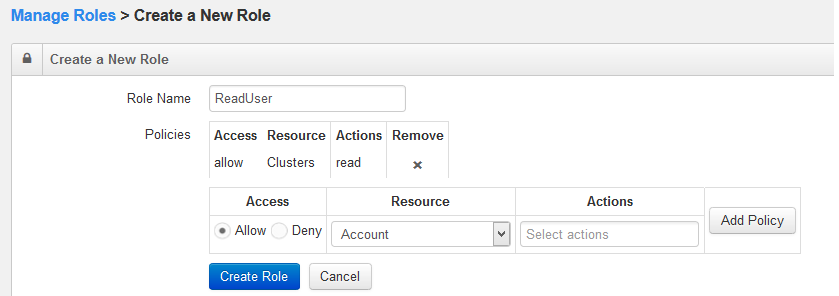
Click Create Role after adding the policy and name. Click Cancel to not create the role.
Cloning a Role¶
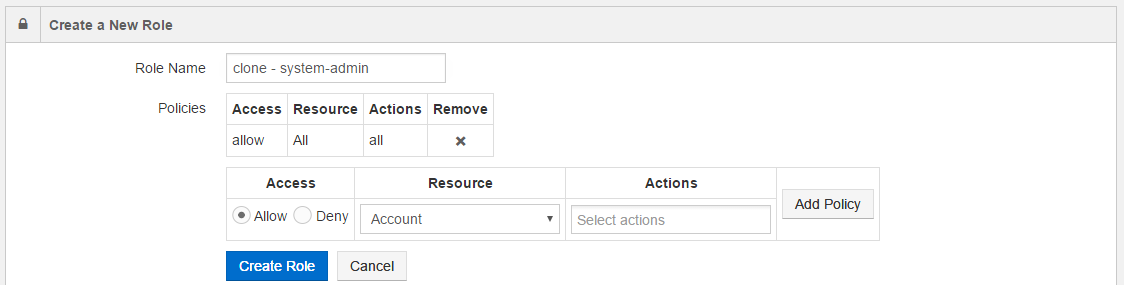
In the Action column of a role, click the down arrow and select Clone to clone that role. The Create a New Role page is displayed with the role name prefixed with clone - and the policies of the parent role, as shown in the following figure.
Modifying a Role¶
In the Action column, click the downward arrow and select Modify to edit a role.
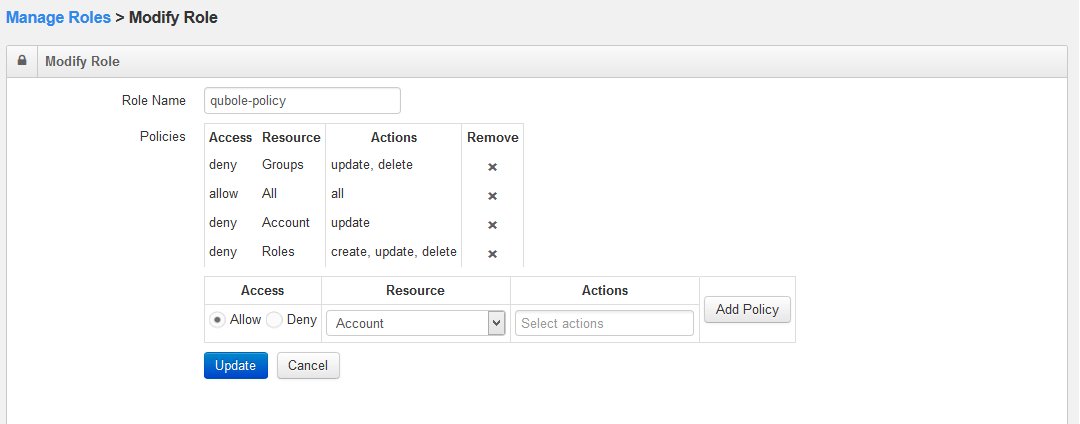
Do the changes and click Update. Click Cancel to retain the previous setting.